Masked FFT and iFFT
The temul.signal_processing module allows one to choose the
masking coordinates with
temul.topotem.fft_mapping.choose_mask_coordinates() and easily
return the masked fast Fourier Transform (FFT) with
temul.topotem.fft_mapping.get_masked_ifft(). This can useful in
various scenarios, from understanding
the diffraction space spots and how they relate to the real space structure,
to revealing domain walls
and finding initial atom positions for difficult images.
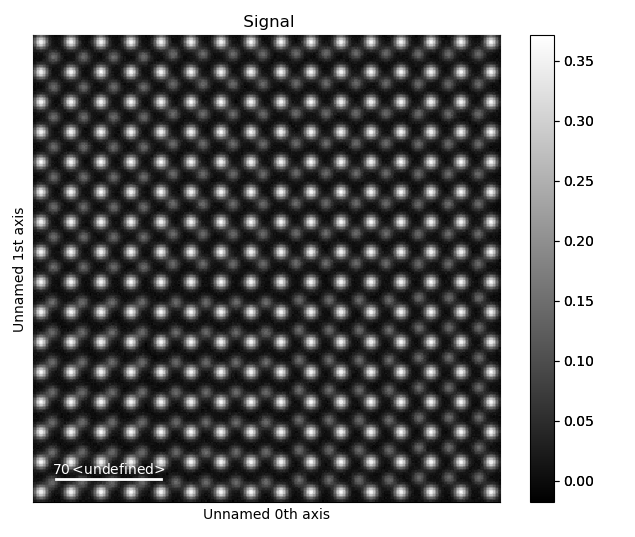
Load the Example Image
>>> import temul.api as tml
>>> from temul.dummy_data import get_polarisation_dummy_dataset
>>> atom_lattice = get_polarisation_dummy_dataset(image_noise=True)
>>> image = atom_lattice.sublattice_list[0].signal
>>> image.plot()
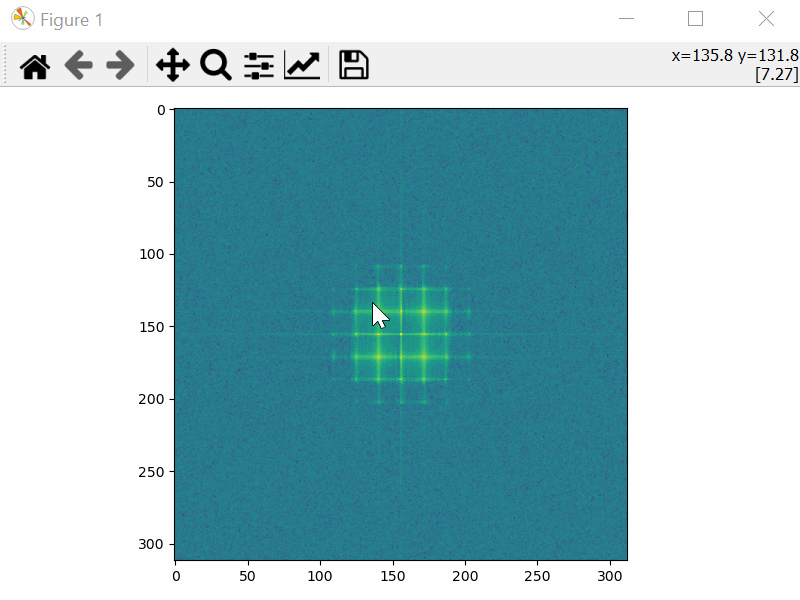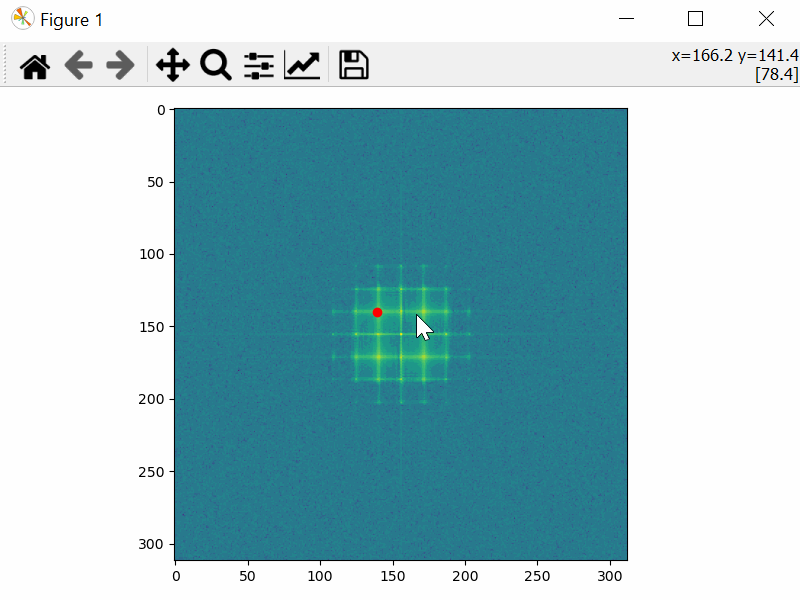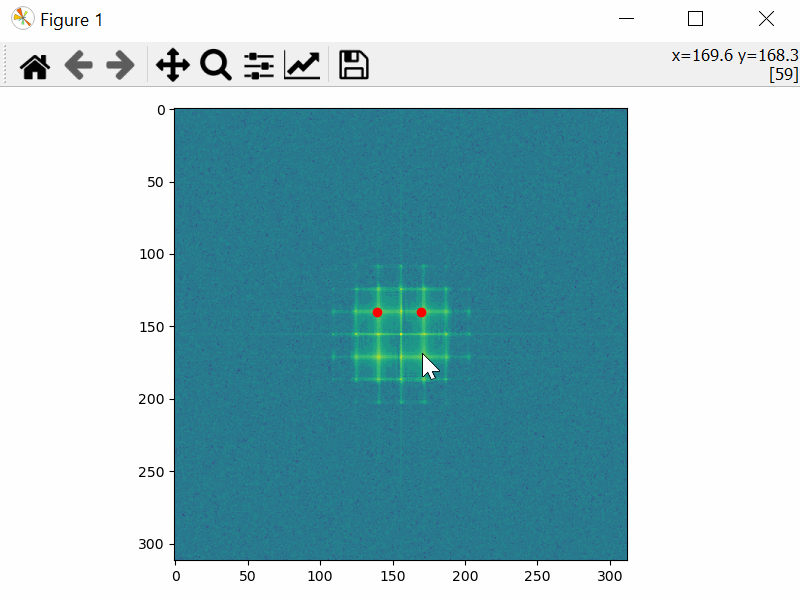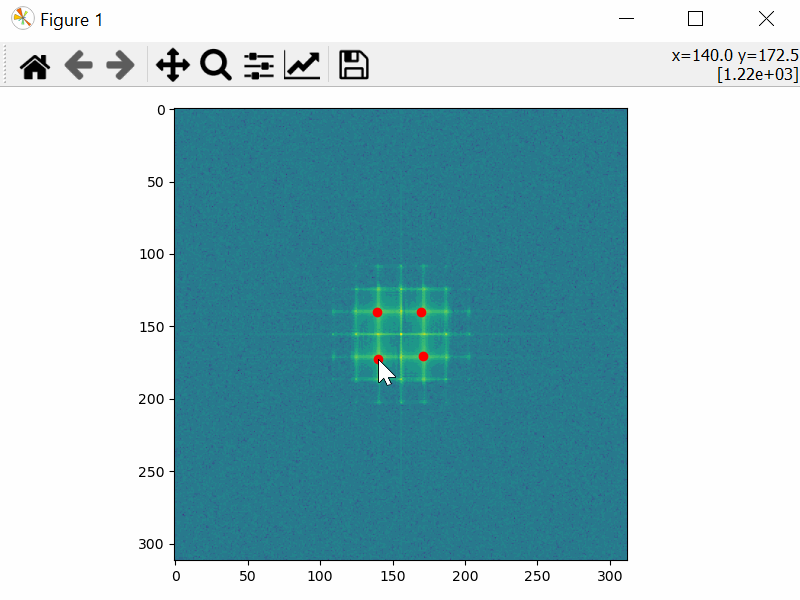
Choose the Mask Coordinates
>>> mask_coords = tml.choose_mask_coordinates(image, norm="log")
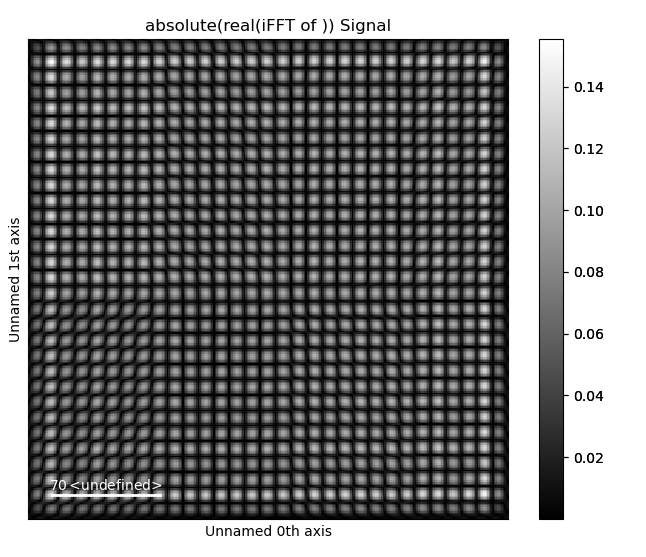
Plot the Masked iFFT
>>> mask_radius = 10 # pixels, default is also 10 pixels
>>> image_ifft = tml.get_masked_ifft(image, mask_coords,
... mask_radius=mask_radius)
>>> image_ifft.plot()
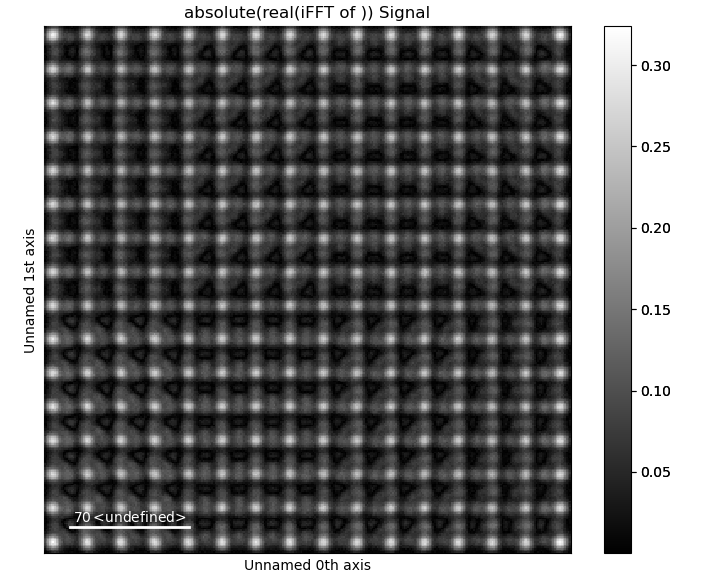
Reverse the masking with keep_masked_area=False
>>> image_ifft = tml.get_masked_ifft(image, mask_coords,
... keep_masked_area=False)
>>> image_ifft.plot()
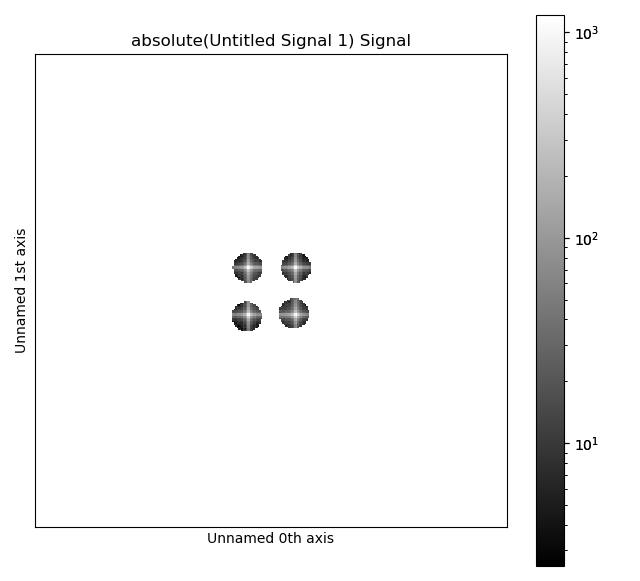
Plot the FFT with masks overlaid by using plot_masked_fft=True
>>> image_ifft = tml.get_masked_ifft(image, mask_coords,
... plot_masked_fft=True)
If the input image is already a Fourier transform
>>> fft_image = image.fft(shift=True) # Check out Hyperspy
>>> image_ifft = tml.get_masked_ifft(fft_image, mask_coords,
... image_space='fourier')
Run FFT masking for Multiple Images
If you have multiple images, you can easily apply the mask to them all in a
simple for loop. Of course, you can also save the images after plotting.
>>> from hyperspy.io import load
>>> for file in files:
... image = load(file)
... image_ifft = tml.get_masked_ifft(image, mask_coords)
... image_ifft.plot()